Think about it. What do you do when you have a problem? You go online and search for a solution. And, what do you do when you find a solution? You buy it.
This is the power of pain-point SEO. When you focus on solving the problems of your website visitors, they will be more likely to do business with you.
So, how can you use pain-point SEO to grow your business? In this blog post, you'll learn more about the difference between traditional SEO and pain-point SEO, and why pain-point SEO will help you grow your search presence—and your business. Next, I'll explain to you in 7 steps how you can do pain-point SEO yourself, including screenshots of the keyword research.
Read on to find out!
The Meaning of Pain-Point SEO
Pain-point SEO is the practice of finding and targeting high-intent keywords that are related to the pain points of your target customers. With this keyword strategy, you can attract leads who are actively looking for solutions to their problems, and therefore are more likely to become customers.
How is Pain-Point SEO Different From Traditional SEO?

At first sight, you might think pain-point SEO isn't that different from traditional SEO. And in a way, you're right. The ultimate goal of both SEO strategies is to increase your search presence. And yes, within modern-day SEO and content strategies, targeting "long-tail keywords" is already explained in every beginner's guide to keyword research.
And yet, I'm dedicating an entire blog post to pain-point SEO, because there's a big but.
The difference between pain-point SEO and traditional SEO is in the focus and, more importantly, the results.
- With traditional SEO, your keyword research starts with listing keywords related to your product or service. With pain-point SEO, your starting point is thinking about the pain points of your target customers.
- Next, traditional SEO prioritizes keywords with high volume and low difficulty. Pain-point SEO, on the other hand, favors keywords that solve a problem. That's why they're also called pain-point keywords. This means that pain point SEO isn't just about ranking for a keyword, but solving the problem your target customer is facing.
- Finally, traditional SEO focuses mainly on traffic, while pain-point SEO focuses on conversion. This means that your traffic may not increase as quickly with Pain-Point SEO as it does with traditional SEO. But since you're attracting leads who're actively looking for solutions to their problems, your conversion rate will be higher.
To put it simply:
Pain-point SEO = attracting high-intent leads by solving their problems
Traditional SEO = attracting traffic by targeting high-volume keywords
Why Can Pain-Point SEO Help You Grow Your Business?
Now that you know what pain-point SEO is and how it's different from traditional SEO, it's time to discuss it what ways it can help you grow your business.
As I've mentioned before, when you focus on solving the problems of your website visitors, they will be more likely to do business with you.
But there's more to it than that.
Pain-point SEO can help you build trust and credibility with your target audience. When you focus your content on solving your audience's problems, you position yourself as an authority in your industry. This, in turn, won't only attract qualified leads, but also make you more attractive to potential business partners or investors.
Pain-point SEO can also help you stand out from your competitors. When you do pain-point-driven keyword research, you can target keywords that your competitors aren't targeting. This gives you a competitive advantage and helps you attract even more qualified leads.
Are you convinced of the power of pain-point SEO? I hope so! In the next section, we will discuss how you can start using it to grow your business.
How to Start Using Pain-Point SEO to Grow Your Business: 7 Steps

Now it's time to put what we've learned into practice. In this section, we will discuss how you can start using pain-point SEO to grow your business.
Before we begin, I want to stress the importance of just getting on with it. It's easy to get stuck at a step, thinking you need to have everything figured out before continuing. But - the most important thing in your SEO strategy is to keep creating quality content. So, if you're not sure about something, just start and figure it out along the way.
Now, let's get into it!
Step 1. Identify your target audience

Who are the people you want to attract to your website? Identifying your target audience is essential in any marketing strategy, and pain-point SEO is no different.
Think about who you want to attract to your website in terms of demographics, geographics, interests, and needs.
Once you've identified your target audience, it's time to move on to the next step.
Step 2. Conduct Target Audience Research

Once you've identified your target audience, it's time to do some research on them.
Try to understand the needs and wants of your target customers. What are their pain points? What are they searching for? The goal here is to gain a good understanding of your target customers, so you can identify pain points to target.
The starting point here depends on the phase of your business.
Existing product or service?
If you have an existing product or service, you can conduct customer surveys or interviews to learn about their needs and pain points. Another great way to generate ideas for pain-point keywords is to look through customer reviews and testimonials. These are a goldmine of information as they can give you insights into the actual problems that your customers are facing.
Things you can ask your customers to get insights into the pain points your product or service solves are:
- What problem were you facing before you found our product/service?
- How did you find out about our product/service?
- What made you decide to try our product/service?
- What other products or services did you consider before making a purchase?
- How has our product/service helped you solve your problem?
- How would you describe our product/service to a friend?
These questions not only give you insights into pain points but also into possible competitors and alternatives your customers considered.
New business?
If you're starting a new business, on the other hand, you can do market research to learn about the needs of your target audience. This might include conducting competitor analysis or reading industry reports. But better: reach out to your target audience directly. This way, you can ask them about their needs and pain points directly. Questions you could ask:
- What needs do you have that are not being met by the current offerings in the market?
- What would be your ideal solution to this problem?
- What are you currently doing to work around this problem?
- How often does this problem occur?
- What is the cost of this problem (in terms of time, money, etc.)?
Other ways to get insights into the needs of your target customers are to look through forums, social media groups, and online communities related to your industry.
Step 3. Identify Pain Points
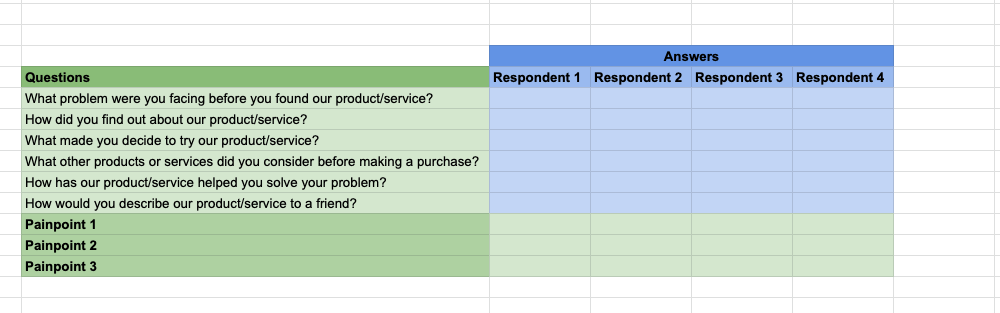
Once you've gathered all the data from your customer or market research, it's time to start identifying pain points.
Take a look at the answers of respondents, and try to uncover at least 1 pain point per respondent, but preferably more.
Once you've noted down all the pain points, it's time to start grouping them in the different stages of the buyer journey.
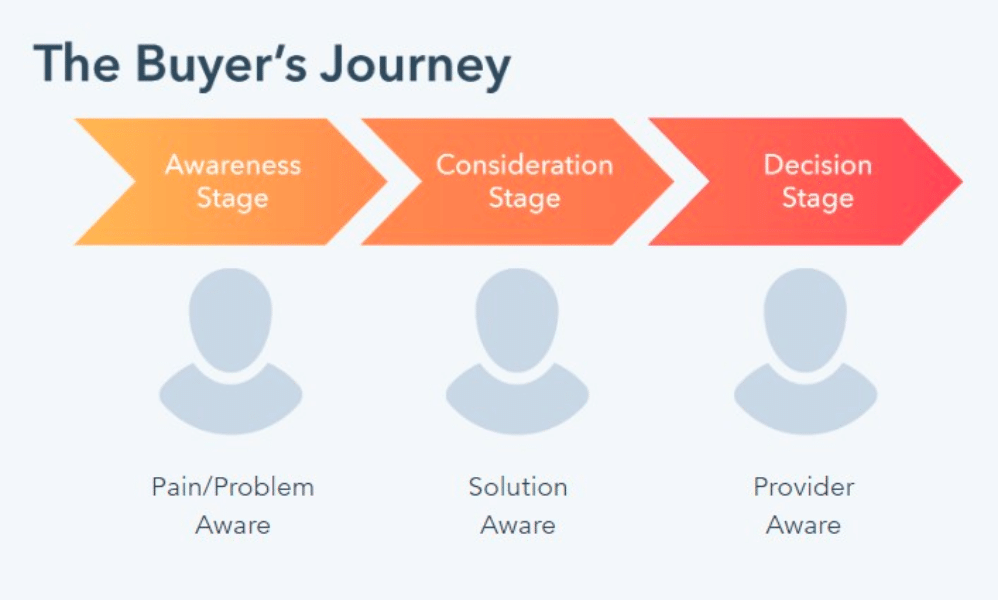
Step 4. Map Out The Buyer Journey
Your customers' pain points may differ at different stages of the buyer journey. Someone who's just starting to research a problem has different pain points than someone who's ready to make a purchase.
The different stages of the buyer journey are typically the following:
Awareness Stage: In this stage, the customer is aware that they have a problem but is not yet sure what the solution is.
Consideration Stage: In this stage, the customer starts researching possible solutions to their problem.
Decision Stage: In this stage, the customer has decided on a solution and is ready to make a purchase.
Now you know the different stages of the buyer journey, you can divide the pain points you discovered in the customer research phase into these stages. This will help you develop a more targeted pain-point SEO strategy.
At this point, you don't need to have any keywords identified yet. To give you an idea of how this works, let's say you are selling a recruitment tooling.
Example of dividing pain points into the buyer journey:
- Awareness Stage: The customer is aware that they are not able to find the best talent and that their current recruitment process is not efficient. Examples of pain point queries at this stage are "How to improve the recruitment process?" or "How to find the best talent?".
- Consideration Stage: The customer is now considering different solutions to their problem. Their pain points at this stage might be something like "What are the best recruitment tools on the market?" or "What are the differences between different types of recruitment software?".
- Decision Stage: The customer is now ready to make a purchase and their pain points might be something like "What are the reviews of recruitment software X?" or "What is the price of recruitment software Y?".
As you can see, the pain points of your customers change as they go through the buyer journey. By targeting different pain points at each stage, you can create a more targeted and effective pain-point SEO strategy.
Step 5. Conduct Keyword Research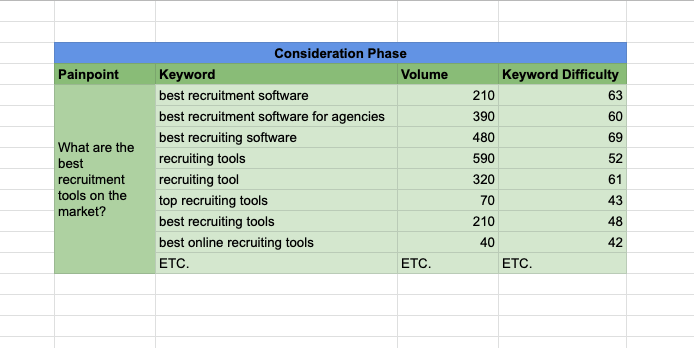
Now you've mapped the different stages of the buyer journey and identified the pain points at each stage, it's time to start doing some keyword research.
Take a look at the pain points you've identified and start brainstorming possible keywords. For example, if you've identified the pain point "How to find the best talent?", a possible keyword could be "talent acquisition". A keyword thus doesn't have to be an exact match of the pain point, but it should be closely related.
Or if you've identified the pain point "What are the best recruitment tools on the market?", a possible keyword could be "best recruitment tools", but also "best recruitment software" or "best recruitment systems". One pain point can thus have multiple keywords associated with it.
Once you've brainstormed a list of potential keywords, it's time to start doing some further research. Check out the search volume and competition for each keyword to prioritize the keywords. If you're not sure how to do that, take a look at our blog post on how to do keyword research.
At this point, it's perfectly fine to prioritize high-volume keywords, as long as they represent a real pain point for your customers. For example: if "best recruitment software" has a higher volume than "best recruitment tools", then "best recruitment software" is probably a better keyword to target.
However, one thing to remember is that keywords with zero volume might still be worth targeting if they are relevant to your business.
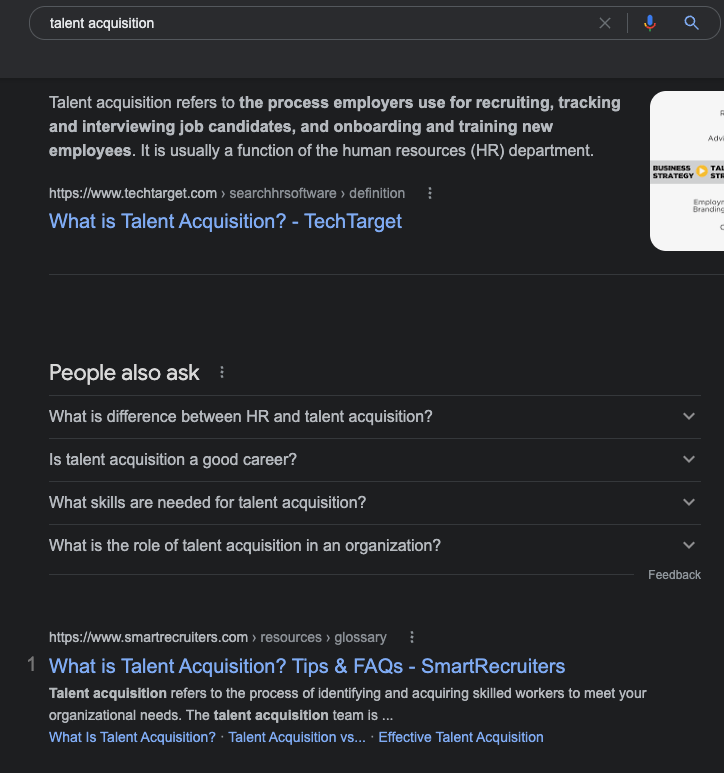
You should also take a look at the SERPs (search engine results pages) for each keyword to see what type of content is currently ranking. This will give you an idea of what you need to do to rank for these keywords.
And more important: it will show you whether the SERP results of the keyword indeed match the identified pain point.
To continue our previous example, if the keyword you choose for the pain point is "talent acquisition", you should check the SERPs to see if the results are indeed providing an answer to "How to find the best talent?". Otherwise, you can better target a different keyword.
Step 6. Deciding on Content Topics

Now that you've done your keyword research, it's time to start creating SEO-friendly content that targets these pain-point keywords.
The type of content framework you should use depends on the buyer journey phase. It's important to be aware of that, as it will help you to provide you with a framework for generating new content.
The different content frameworks for the buyer journey stages are:
Awareness stage:
- How-to articles: content that covers a specific problem and how to solve it. Example: How to improve your recruitment process
- Thought leadership posts: content that covers a specific topic in depth. This type of content is typically longer than other types of content and is aimed at helping the reader understand a topic better. Example: Recruitment Trends in 2022
Consideration stage:
- Comparison posts: content that compares different products, services, or solutions. Example: Recruit'Em and OctoHR Compared
- Best products or service lists: content that showcases the best products or services in a specific category. Example: The Best Recruitment Software of 2022
- Alternatives posts: content that covers different alternatives to a specific product, service, or solution. Example: Alternatives to Recruit'Em
Decision stage:
- Product/service use case: content that covers how to use a specific product or service. Example: How to Use *YOUR RECRUITMENT TOOL* for Effective Talent Sourcing
- Reviews: content that covers reviews of a specific product or service. Example: Recruit'Em Review. Yes, you can write a review about your competitor's product, to end with a CTA to your product as an alternative!
- Pricing posts: content that covers the pricing of a specific product or service. For example, if your competitor isn't transparent about their pricing on their website, you can write a post about it.
When deciding on what type of post to use for a certain pain point, again take a look at the SERP results for that keyword. This will give you an idea of what's already ranking and what you need to do to rank.
Once you've decided on the type of content you're going to create, it's time to start writing!
Step 7. Start writing!

When creating your pain-point SEO content, there are a few things you need to keep in mind about your content strategy:
- Your content needs to be high-quality: This means that your content needs to be well-researched, well-written, and comprehensive.
- Your content needs to be relevant: This means that your content needs to be relevant to the keyword you're targeting and the pain point you're trying to address.
- Your content needs to be unique: This means that your content needs to be unique and different from what's already out there.
Now that you know what you need to do, it's time to start writing. Keep in mind that it might take a few tries to get it right. But, with some practice, you'll be a pain-point SEO pro in no time!
Final Thoughts
Pain-point SEO is a great way to grow your business by addressing the needs of your target customers. By targeting pain-point keywords, you can attract leads who are actively looking for solutions to their problems. And, by creating high-quality, relevant, and unique content, you can help them find the answers they're looking for!

 13 min read
13 min read





 10 min read
10 min read

